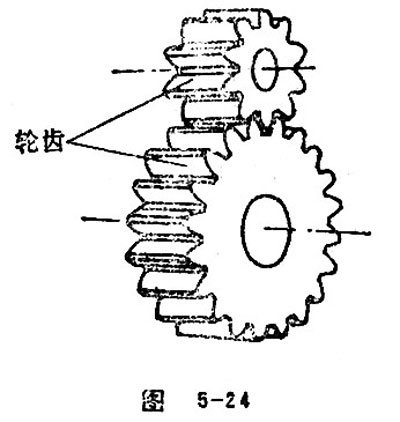
Gear Teeth
Every bulge in a gear used in meshing is called gear teeth, teeth, for short.
Tooth Depth
Tooth depth refers to the radial distance (h) between addendum circle and dedendum circle. See Figure 5-25.
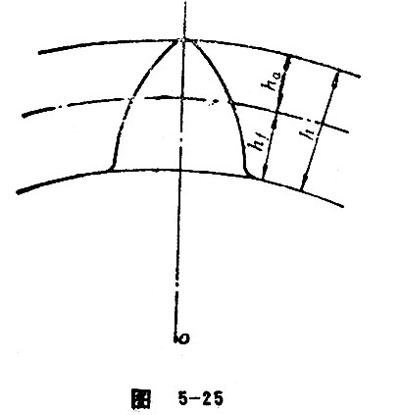
Tooth depth includes addendum and dedendum. The formula is![]() . The
. The![]() here is the coefficient of variation of the addendum circle.
here is the coefficient of variation of the addendum circle.
Addendum
Addendum refers to the radial distance (h) between addendum circle and reference circle (see Figure 5-25). The value is![]() . Here,
. Here, ![]() is the coefficient of variation of addendum circle.
is the coefficient of variation of addendum circle.
Dedendum
Addendum refers to the radial distance (h) between dedendum circle and reference circle (see Figure 5-25). The value is![]() .
.
Working Depth
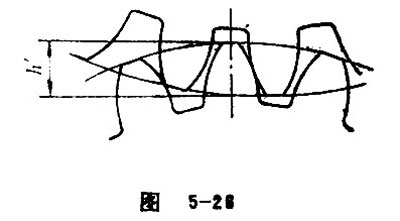
Each of the tip cylinders of the two mating gears has an intersection point with the line of centers. The shortest distance of the two intersection points is called working depth. See Figure 5-26.
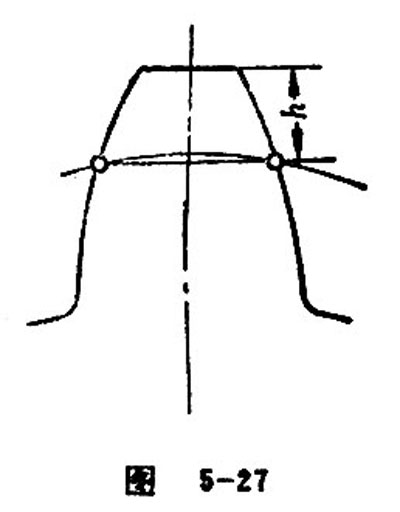
Chordal Height
Chordal height refers to the shortest distance from the center point of normal chordal tooth thickness to the crest. See Figure 5-27.
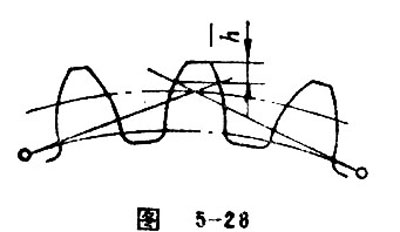
Constant Chord Height
Constant chord height refers to the shortest distance between the center point of constant chord and the top land (see Figure 5-28). The formula for constant chord height is:
Standard involute cylindrical gear:
![]()
As for external gear, Δh=0; As for internal gear, ![]() ,
,![]() , when α=20 and
, when α=20 and ![]() ,
, ![]()
Modified involute cylindrical gear:
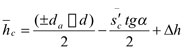 . In this formula, as for “±”和“
. In this formula, as for “±”和“”, the upper symbols are applied in external gear while the lower symbols applied in internal gear.
When α=20, 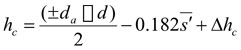 , for external gear, Δh=0; for internal gear,
, for external gear, Δh=0; for internal gear, 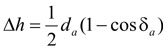 ,
,![]() .
.
Full-depth Tooth
Generally, full-depth tooth refers to the tooth depth with the addendum coefficient (h*a) being 1. With many merits, full-depth tooth is the most widely used depth nationwide.
High Tooth
High tooth is higher than full-depth tooth. High tooth refers to those whose addendum coefficient is higher than 1. This kind of tooth height is flexible and it has larger overlap ratio. But until now it is rarely used and under research.
Shortened Tooth
The tooth depth of shortened tooth is shorter than full-depth tooth. Generally, it refers to the tooth depth whose addendum coefficient is shorter than 1. Some countries stipulate standards for this kind of tooth. As it has few merits, it is rarely used except for special cases.
Intersection Circle(of Opposed Involutes)
Intersection circle (of opposed involutes) refers to the circle which is made by taking distance from the intersection of left and right side tooth profile of the transverse tooth of spur gear (or equivalent spur gear) to the axial line as semi diameter. See Figure 5-29.
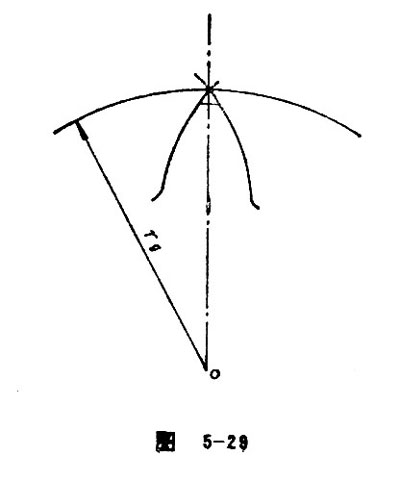
Face Width
Face width refers to the distance measured along the direction of reference cylindrical generatrix in the toothed portion of the gear. See Figure 5-30.
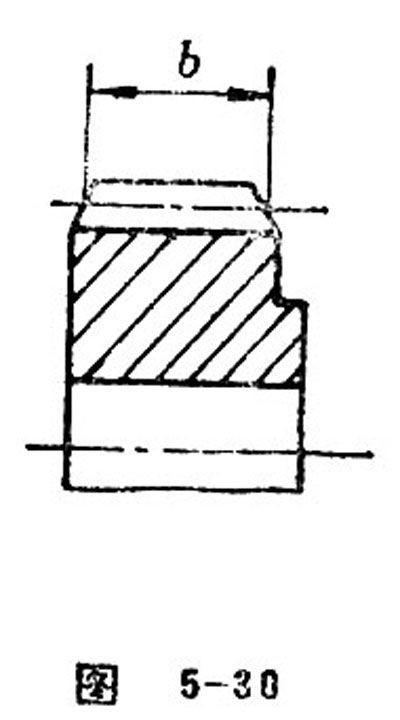
Effective Face Width
Effective face width refers to the contacting width of a pair of meshing gears.
To ensure that the effective face width is no less than the face width affirmed during the calculation of strength, what is generally prescribed is that to take the width of bull gear as the face width of strength calculation. The face width of pinion gear is bigger than that of bull gear for 5-10mm. See Figure 5-31.
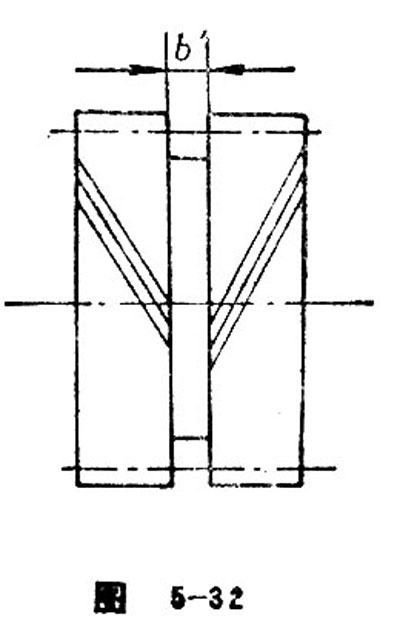
Empty Tool Flute
Empty too flute refers to the non-tooth flute between the left and right side of duplicate gear or herringbone gear (Figure 5-32).